Did you know that making simple lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on preventing arteriosclerosis and maintaining a healthy heart? Arteriosclerosis, also known as hardening of the arteries, occurs when plaque builds up in the arterial walls, restricting blood flow to vital organs.However,by adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress, and prioritizing sleep, you can mitigate the risk of arteriosclerosis and promote cardiovascular health.
Arteriosclerosis is a heart disease that occurs when the arteries, the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body, become thickened and stiff. It is characterized by thickening and hardening of artery walls, leading to reduced blood flow and potential complications.
Arteriosclerosis is a broad term that includes three main types: atherosclerosis, Munchberg arteriosclerosis, and arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the most common form and is often used interchangeably with arteriosclerosis.

Arteriosclerosis is a hardening of the arteries that affects smaller arteries and arterioles. It is often associated with high blood pressure and is often accompanied by other health conditions, such as diabetes and kidney disease. Arteriosclerosis can lead to organ damage because reduced blood flow deprives tissues of oxygen and nutrients.
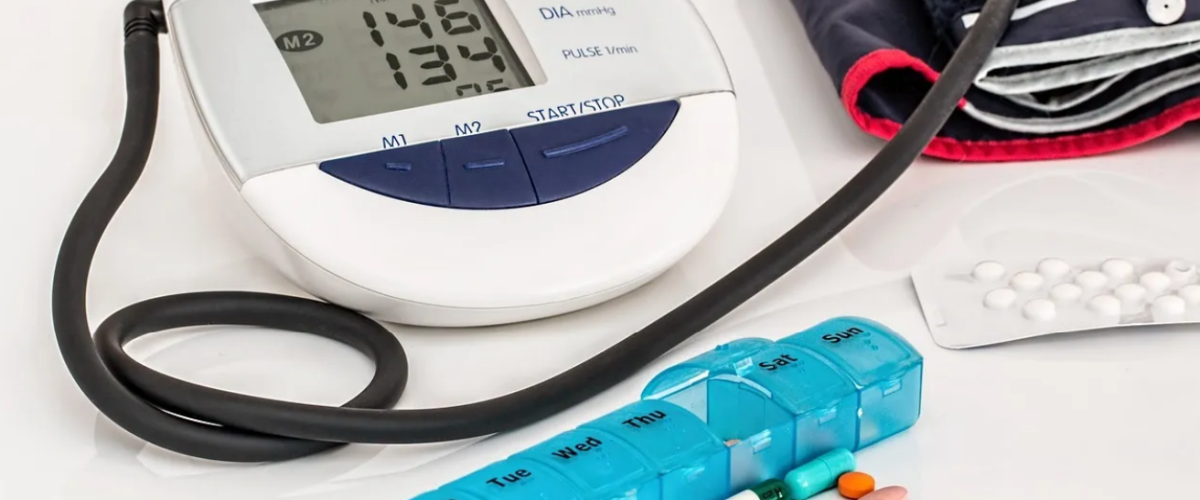
Diagnosing arteriosclerosis usually involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic testing. A medical professional may order blood tests to assess cholesterol levels, order imaging tests such as ultrasound or angiography, or recommend a coronary angiogram to accurately assess the extent of the blockage in the arteries.
Treatment of arteriosclerosis aims to control symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and reduce the risk of complications. Lifestyle changes are often recommended, including adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and effectively managing diabetes.
Arteriosclerosis usually causes no symptoms until complications occur. Symptoms vary depending on the problem and may include:
● Fatigue and weakness
● Chest pain
● Shortness of breath
● numbness and weakness of limbs
● Slurred speech or difficulty communicating
● Pain when walking
● One of the main causes of arteriosclerosis is the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. Plaque is made up of cholesterol, fat, calcium and other substances that build up on the lining of your arteries over time. This buildup narrows the arteries, restricting the flow of blood and oxygen to organs and tissues. Eventually, it can lead to complete blockage of the arteries, leading to serious health problems.
● High levels of cholesterol in the blood play an important role in the development of arteriosclerosis. When there is too much cholesterol, it can deposit on artery walls, triggering the formation of plaque. This excess cholesterol usually comes from a diet rich in saturated fats and trans fats, which are commonly found in processed foods, fried foods, and fatty meats.
● Another important cause of arteriosclerosis is high blood pressure. When blood pressure remains high, it puts extra pressure on arteries, weakening their walls and making them more susceptible to damage. Increased pressure can also cause rough plaque to appear on artery walls, providing an ideal environment for plaque to build up.
● Smoking is a well-known risk factor for arteriosclerosis. Cigarette smoke contains harmful chemicals that can directly damage arteries and promote plaque formation. Smoking also reduces the overall amount of oxygen in the blood, making it harder for the arteries to function properly and causing them to deteriorate over time.
● Lack of physical activity is another root cause of arteriosclerosis. Regular exercise helps keep artery walls flexible and healthy, improves blood flow and reduces the risk of plaque buildup. On the other hand, sedentary behavior can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels, all of which are risk factors for arteriosclerosis.
● Genetics and family history also play a role in determining an individual's susceptibility to atherosclerosis. If an immediate family member has a history of cardiovascular disease, the chance of developing arteriosclerosis is higher. While genes cannot be changed, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing other risk factors can help reduce the impact of genetic predispositions.
● Finally, certain diseases, such as diabetes and obesity, increase the risk of arteriosclerosis. Diabetes causes high blood sugar, which damages artery walls and promotes plaque buildup. Likewise, obesity puts additional stress on the cardiovascular system and increases the likelihood of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.


Magnesium is an important nutrient and an important mineral for the human body, involved in many physiological processes. Magnesium helps relax the smooth muscles within artery walls and balance mineral levels. Plays a key role in maintaining cardiovascular health, primarily by regulating blood pressure and supporting healthy blood vessels.
Some excellent sources of magnesium include dark leafy green vegetables (such as spinach and kale), nuts and seeds (such as almonds and pumpkin seeds), whole grains, legumes, and fish. Additionally, magnesium supplements are available for those who have difficulty meeting their daily needs through diet alone. Magnesium comes in many forms, so you can choose the type that's right for you. Typically, magnesium can be taken orally as a supplement. Magnesium malate, Magnesium Taurate and Magnesium L-Threonate are more easily absorbed by the body than other forms such as magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate.
Turmeric contains an active ingredient called curcumin, and studies claim that turmeric has antithrombotic (prevents blood clots) and anticoagulant (blood thinner) abilities.
Furthermore, OEA's ability to modulate appetite and lipid metabolism may provide additional benefits to patients with obesity, a major risk factor for atherosclerosis. By promoting fat oxidation and lowering cholesterol levels, OEA may aid in weight management, thereby preventing the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaque.
Q: What does a healthy diet for preventing arteriosclerosis look like?
A: A healthy diet for preventing arteriosclerosis includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It should limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars.
Q: What types of physical activities can help prevent arteriosclerosis?
A: Engaging in regular aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling can help prevent arteriosclerosis. Resistance training and flexibility exercises are also beneficial.
Disclaimer: This article is for general information only and should not be construed as any medical advice. Some of the blog post information comes from the Internet and is not professional. This website is only responsible for sorting, formatting and editing articles. The purpose of conveying more information does not mean that you agree with its views or confirm the authenticity of its content. Always consult a health care professional before using any supplements or making changes to your health care regimen.
Post time: Oct-11-2023