Spermidine, a natural compound, has received much attention due to its ability to induce autophagy, which can help cells remove harmful proteins and cellular waste, thereby promoting cell renewal and enhancing overall health. In this article on In our comprehensive guide to spermidine, let's take a closer look at the connection between spermidine and our own health!
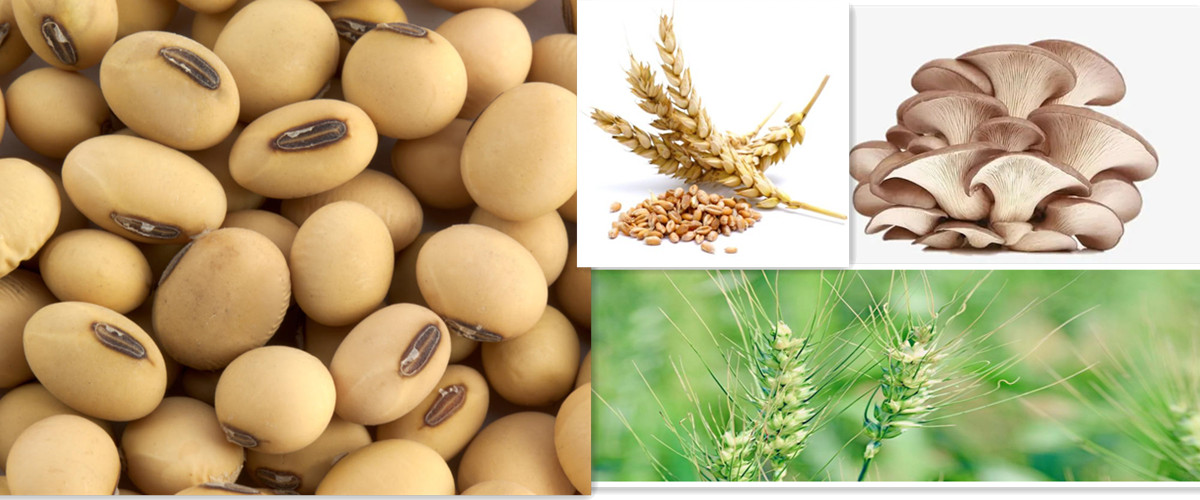
So, what is spermidine? Derived from the Greek word "sperma", meaning seed, spermidine is widely found in plant sources such as soybeans, peas, mushrooms and whole grains. It is also found in aged cheeses that have undergone a fermentation and aging process that results in higher levels of spermidine.
Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its formation from putrescine. It is a precursor of other polyamines such as spermine and its structural isomer pyrospermine.
As a naturally occurring polyamine, spermidine plays a vital role in various cellular functions. It is found in all organisms from bacteria to plants and animals, and is especially abundant in human cells.
Obtaining adequate levels of spermidine through diet alone is challenging. In recent years, research on this organic compound has led to the production of spermidine supplements. These supplements provide a convenient and reliable way to ensure adequate spermidine intake, especially for those who may not have access to spermidine-rich foods.
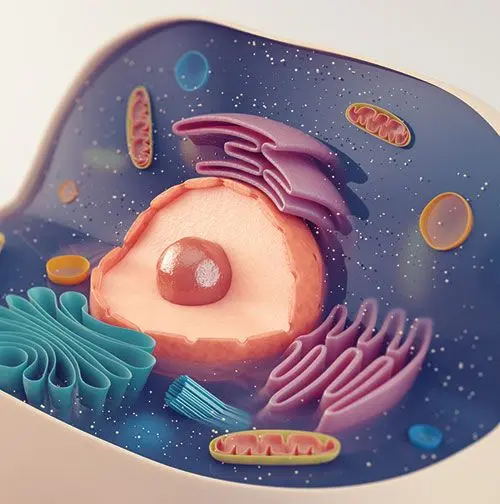
1. Enhance the ability of autophagy
Autophagy is a process responsible for the removal of damaged or unnecessary cellular components and is critical for maintaining cellular health and function.
Spermidine has been found to stimulate autophagy, promoting the elimination of harmful substances and improving overall cellular integrity. This, in turn, has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases and certain types of cancer.
2. Has a certain cardioprotective effect.
Several studies have shown that spermidine can help lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve cardiovascular health.
Spermidine does this by preventing the buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels, reducing inflammation and promoting the regeneration of damaged heart cells. By incorporating spermidine into our diet, we may protect ourselves from heart-related diseases.
3. Shows promise in promoting brain health.
Aging is often associated with a decline in cognitive function, leading to diseases such as dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
However, spermidine was found to counteract these effects by protecting neurons from oxidative stress and improving their overall survival.
Studies in animal models have even shown that supplementation with spermidine can delay age-related decline in memory and learning. Therefore, harnessing the potential of spermidine could pave the way for new prevention strategies and interventions in neurodegenerative diseases.
Below are some top food sources of spermidine that you may want to consider adding to your diet to increase your spermidine intake.
1. Wheat Germ
It contains a high content of spermidine. Often used as a topping in cereal or yogurt, adding wheat germ to your morning diet is an easy way to reap the benefits of spermidine.
2. Soy
Not only is soy an excellent choice of vegetable protein, but it also contains a lot of spermidine. Introducing soy products like tofu, tempeh or edamame into your diet is an excellent way to increase your intake of this beneficial compound.
3. Mushrooms
Shiitake, portobello mushrooms, and oyster mushrooms are especially rich in this compound. These versatile ingredients can be used in a variety of dishes from stir frys to soups, providing a delicious and nutritious way to increase spermidine consumption.
4. Other
Other spermidine-rich foods include legumes such as lentils, chickpeas and green peas, and certain fruits such as grapefruit, oranges and pears. By including these foods in your diet, you can naturally increase your spermidine intake and potentially exert its health-promoting effects.
While research on spermidine is still ongoing, initial results are promising. It's worth noting that spermidine levels may vary based on factors such as food processing, ripeness, and cooking method. Therefore, to maximize intake, it is recommended to consume these foods in their freshest and least processed forms.
Most people are not very clear about the difference between getting spermidine from food or using spermidine supplements directly, let's take a look at the difference together!
1. Supplements offer a convenient way to increase spermidine levels, especially for those who struggle to get enough through their regular diet. Spermidine supplements usually come from natural sources and come in different forms, such as capsules or powder. These supplements go through a process of concentrating spermidine, making it easier to obtain higher doses than food alone.
2. When consuming foods rich in spermidine, you benefit from the synergy of other nutrients present in the food matrix, which enhances its absorption and overall health benefits. Also, dietary sources often provide lower amounts of spermidine compared to supplements, but are still beneficial.
3. The supplement provides a higher and standardized dose of spermidine, allowing for a more targeted approach based on individual needs. This is especially beneficial for individuals seeking the specific health benefits of spermidine or for individuals who restrict their consumption of certain spermidine-rich foods due to dietary restrictions.
The choice of obtaining spermidine from food or supplements depends on personal preference and situation. For most people, a balanced diet that includes foods rich in spermidine should provide adequate levels of this beneficial compound. However, for those seeking higher concentrations or facing dietary restrictions, supplementation can be a valuable addition.
Determining the ideal dose of spermidine depends on many factors, including age, general health, and the specific desired results.
Currently, there is no recommended daily intake (RDI) for spermidine. Studies show beneficial effects at doses of 1 to 10 mg per day. However, it is always recommended to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating spermidine into your daily routine.
Natural food sources provide spermidine and can be an excellent addition to your diet. Foods such as wheat germ, certain fruits (grapefruit, grapes, and oranges), cheese, soybeans, mushrooms, and even aged wine contain large amounts of spermidine. Including these foods in a balanced diet can help increase spermidine intake naturally.
Supplements are also an option for those seeking additional intake of spermidine. Spermidine supplements come in many forms, including capsules and powders. High-quality supplements should come from reliable manufacturers who adhere to strict quality control standards.
When starting spermidine supplementation, it is recommended to start with a low dose. Starting with about 1 mg per day and gradually increasing the dose over several weeks can help avoid potential side effects.
Although spermidine appears to be generally safe and well tolerated, some people may experience mild gastrointestinal effects such as bloating or stomach upset when first supplemented with spermidine. If these symptoms persist or worsen, a healthcare professional must be consulted.
Q: How long does it take for spermidine to work?
A: The time it takes spermidine to work and produce visible results may vary based on a number of factors, including an individual's age, overall health, dosage, and duration of supplementation. In general, continued spermidine supplementation may be required for several weeks or even months before an individual begins to notice any significant changes.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any supplements or changing your healthcare regimen.
Post time: Jun-28-2023