Dopamine is a fascinating neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in the brain's reward and pleasure centers. Often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical, it is responsible for a variety of physiological and psychological processes that influence our overall mood, motivation, and even addictive behaviors.
Dopamine, often referred to as the "feel good" neurotransmitter, was first discovered in the 1950s by Swedish scientist Arvid Carlsson. It is classified as a monoamine neurotransmitter, which means it is a chemical messenger that carries signals between nerve cells. Dopamine is produced in several areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus of the brain.
The main function of dopamine is to transmit signals between neurons and influence various body functions. It is thought to regulate movement, emotional responses, motivation, and feelings of pleasure and reward. Dopamine also plays an important role in various cognitive processes such as learning, memory, and attention.
When dopamine is released into the brain's reward pathways, it produces feelings of pleasure or satisfaction.
During moments of pleasure and reward, we produce large amounts of dopamine, and when levels are too low, we feel unmotivated and helpless.
Additionally, the brain’s reward system is closely tied to dopamine. The role of neurotransmitters is to promote feelings of enjoyment and reinforcement, thereby generating motivation. Pushing us to achieve our goals and seek rewards.
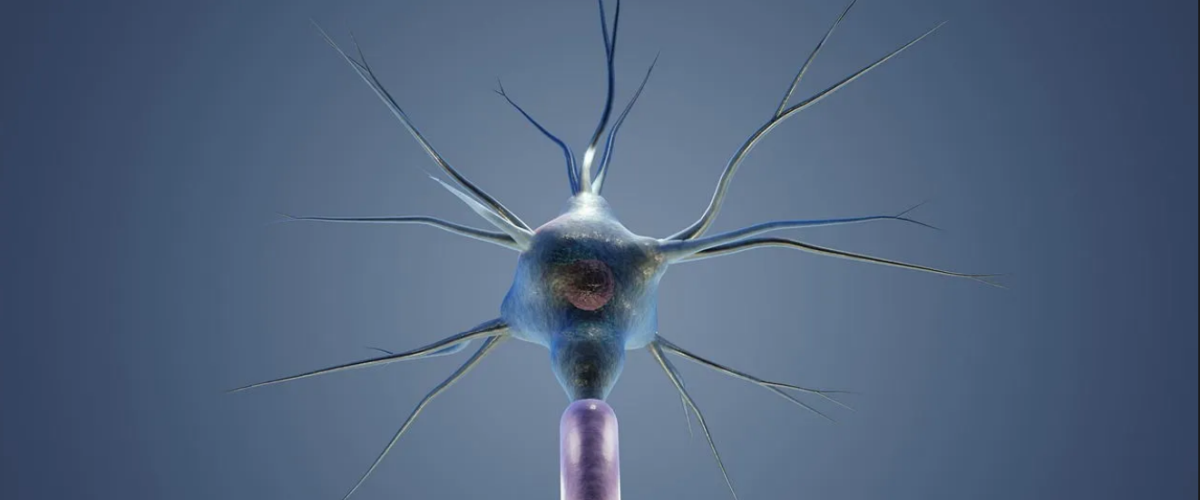
Dopamine is produced in multiple areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area. These areas act as dopamine factories, producing and releasing this neurotransmitter into different parts of the brain. Once released, dopamine binds to specific receptors (called dopamine receptors) located on the surface of the receiving cell.
There are five types of dopamine receptors, labeled D1 to D5. Each receptor type is located in a different brain region, allowing dopamine to have different effects. When dopamine binds to a receptor, it excites or inhibits the activity of the receiving cell, depending on the type of receptor to which it is attached.
Dopamine plays a crucial role in regulating movement in the nigrostriatal pathway. In this pathway, dopamine helps control and coordinate muscle activity.
In the prefrontal cortex, dopamine helps regulate working memory, allowing us to hold and manipulate information in our minds. It also plays a role in attention and decision-making processes. Imbalances in dopamine levels in the prefrontal cortex have been linked to conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and schizophrenia.
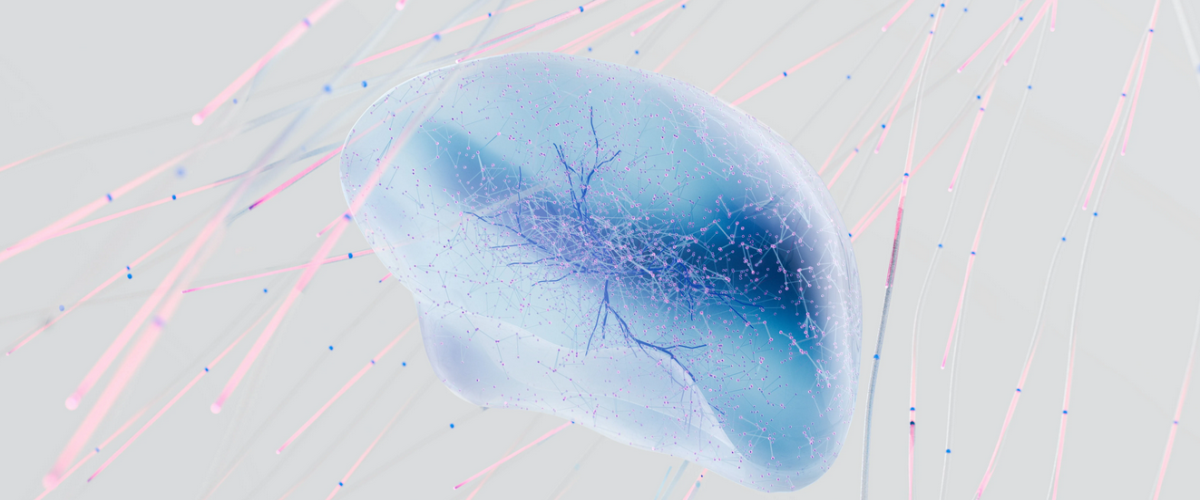
The release and regulation of dopamine is tightly controlled by the brain to maintain balance and ensure normal function. A complex system of feedback mechanisms, involving other neurotransmitters and brain regions, regulates dopamine levels.

Dopamine is a chemical messenger, or neurotransmitter, in the brain that carries signals between nerve cells. It plays a vital role in a variety of brain functions, including regulating movement, mood, and emotional responses, making it an important component of our mental health. However, an imbalance in dopamine levels can lead to a variety of mental health issues.
● Research shows that people with depression may have lower dopamine levels in certain brain areas, leading to reduced motivation and enjoyment in daily activities.
● Imbalanced dopamine levels can lead to anxiety disorders. Increased dopamine activity in certain brain areas can lead to increased anxiety and restlessness.
● Excessive dopamine activity in specific brain regions is thought to contribute to symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions.
● Drugs and addictive behaviors often increase dopamine levels in the brain, causing euphoric and rewarding feelings. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on these substances or behaviors to release dopamine, creating a cycle of addiction.


Q: Can medication be used to regulate dopamine levels?
A: Yes, certain medications, such as dopamine agonists or dopamine reuptake inhibitors, are used to treat conditions related to dopamine dysregulation. These medications can help restore dopamine balance in the brain and alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like Parkinson's disease or depression.
Q: How can one maintain a healthy dopamine balance?
A: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a nutritious diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management, can contribute to optimal dopamine regulation. Engaging in enjoyable activities, setting achievable goals, and practicing mindfulness can also help maintain a healthy dopamine balance.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any supplements or changing your healthcare regimen.
Post time: Sep-15-2023