Magnesium is an essential mineral that our bodies need to function properly, but is often overlooked. It plays a vital role in many body processes, including energy production, muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood pressure regulation, among others. Therefore, it is important to ensure adequate magnesium intake through diet or supplements in daily life.
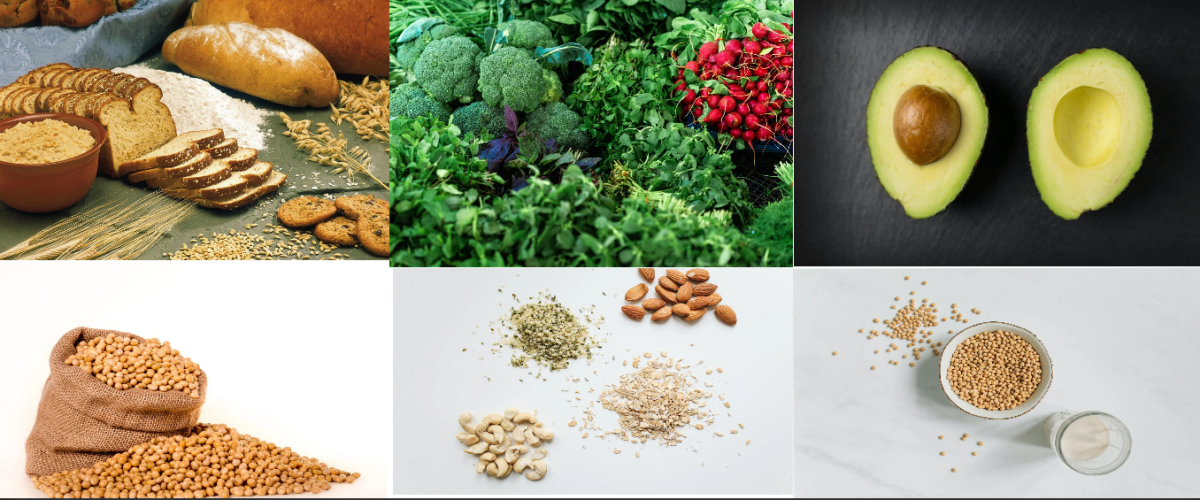
Some of the best dietary sources of magnesium include nuts and seeds, dark green leafy vegetables, legumes, whole grains and certain types of fish. Regular consumption of these foods can help replenish a certain amount of magnesium, but the magnesium content of most people's diets is not very high, which can have some negative effects on personal health.
For those who have difficulty meeting their magnesium needs through diet alone, magnesium supplements can benefit health in several ways and come in forms such as magnesium oxide, magnesium threonate, magnesium taurate, and magnesium glycinate. However, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen to avoid potential interactions or complications.
So, what is magnesium? Magnesium is an important mineral and the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body. It is involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions that regulate various bodily functions, including energy production, protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood pressure regulation, and DNA synthesis. Magnesium acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in these processes, making it essential for optimal health.

Magnesium is an important mineral that plays an important role in good health. Our bodies typically get magnesium from dietary sources such as green leafy vegetables, nuts, legumes and whole grains.
However, magnesium deficiency can occur due to poor dietary choices, increased consumption of processed foods, and certain medical conditions. It is estimated that approximately 50-60% of adults do not meet the recommended daily intake of magnesium.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency:
● Muscle spasms and spasms
● Fatigue and weakness
● Irregular heartbeat
● Mood swings and mental health problems
● Insomnia and sleep disorders
● Osteoporosis and poor bone health
● High blood pressure

Spinach and green leafy vegetables
Dark leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium. They are not only rich in various vitamins and minerals, but also provide a lot of dietary fiber. Spinach, in particular, is a good source of magnesium, with just one cup providing nearly 40 percent of your daily recommended intake. Incorporating these greens into your diet can be as simple as adding them to salads, smoothies, or sautéing them as a side dish.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only delicious snacks, but also a great source of magnesium. Almonds, cashews, and Brazil nuts are particularly high in magnesium. Additionally, pumpkin seeds, flax seeds, and chia seeds are also rich sources of this mineral. Adding a handful of nuts and seeds to your daily routine, either as a snack or as part of a meal, can provide you with plenty of magnesium as well as healthy fats and proteins.
avocado
In addition to being a trendy superfood, avocados are also an excellent source of magnesium. Thanks to their smooth, creamy texture, they are a versatile addition to your diet. Avocados provide not only a healthy dose of magnesium, but also plenty of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat, fiber and other essential nutrients. Adding sliced avocado to salads, using mashed avocado as a spread or enjoying it in guacamole are all delicious ways to boost your magnesium intake.
Beans
Legumes such as black beans, chickpeas, lentils, and soybeans are nutrient-dense plant-based sources of magnesium. Not only are they rich in magnesium, but they also provide a variety of other essential nutrients, including fiber and protein. Incorporating beans into your diet can be done by adding them to soups, stews or salads, making bean burgers or simply enjoying them as a side dish with your main meal.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats are not only high in fiber, but also an excellent source of magnesium. You can significantly increase your magnesium intake by replacing refined grains with whole grains in your diet. These grains can be used as the base of salads, enjoyed as a side dish, or incorporated into a variety of recipes, such as quinoa bowls or oatmeal breakfasts.
Magnesium needs vary from person to person, depending on age, sex, health, and other factors.By incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your daily diet, you can help individuals get the magnesium they need, but some people who don’t have a healthy diet don’t get enough magnesium, so magnesium supplements can be a great way to a better option
Magnesium comes in many forms, so you can choose the type that's right for you based on your needs. Typically, magnesium is taken orally as a supplement.
Magnesium L-Threonate, Magnesium Citrate, Magnesium Malate, and Magnesium Taurate are more easily absorbed by the body than other forms, such as magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate.
Q: Can magnesium support mental health?
A: Yes, magnesium is known to have a calming effect on the nervous system, which can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Adequate magnesium levels have been associated with improved mood and better overall mental well-being.
Q: How can I increase my magnesium intake naturally?
A: You can increase your magnesium intake by consuming magnesium-rich foods such as leafy greens (spinach, kale), nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds), legumes (black beans, lentils), and whole grains (brown rice, quinoa). Alternatively, you can also consider taking magnesium supplements after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any supplements or changing your healthcare regimen.
Post time: Sep-12-2023